|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Properties of CAPRI targets |
|||||
|
|
|
a |
b |
PDP-based Rank of near-native complexc |
MJ-based Rank of near-native complexc |
|
1 |
HPr kinase / HPr |
102 |
8 |
4 |
5 |
|
2 |
rotavirus VP6 / Fab |
88 |
4 |
7 |
5 |
|
3 |
hemagglutinin / Fab HC63 |
90 |
4 |
48 |
18 |
|
4 |
a-amylase / camelide VH_1 |
66 |
1 |
2 |
40 |
|
5 |
a-amylase / camelide VH_2 |
65 |
1 |
3 |
27 |
|
6 |
a-amylase / camelide VH_3 |
65 |
9 |
4 |
4 |
|
7 |
T cell receptor / exotoxin A |
70 |
19 |
1 |
8 |
|
8 |
Nidogen-G3/laminin EGF |
179 |
12 |
3 |
6 |
|
9 |
LicT homodimer |
162 |
32 |
1 |
1 |
a Number of predicted complexes submitted for each CAPRI target.
b Number of correctly predicted (hit) structures among those submitted.
c Near-native is defined by RMSD
£ 10 Å.
Docking
potentials differ from folding potentials
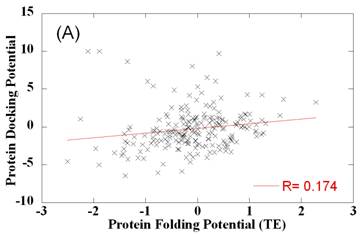
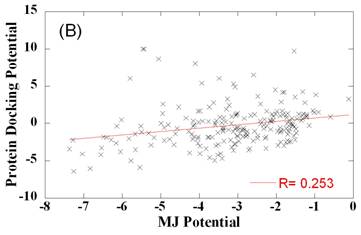
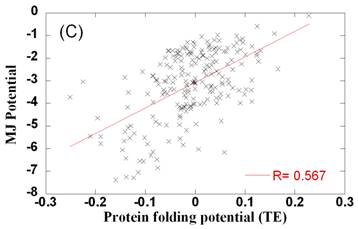
Comparison of side chain-side chain contact potentials for protein docking and protein folding. Panel A and B compare the optimally designed PDPs (ordinate) with the TE (panel A) and MJ (panel B) potentials derived from folded structures. Weak correlation is observed between the two sets. Panel C compares the two sets of folding potentials. The best fitting lines and correlation coefficients are shown on the panels.
